Quick Installation of FastGpt AI Knowledge Base
FastGpt is recommended to deploy with Docker on Git, so it is also easy to deploy on Sealos conveniently. FastGpt relies on MongoDB and PostgreSQL. The following tutorial only describes how to deploy these two databases and the FastGpt image on Sealos. The environment variables and usage instructions of FastGpt will not be explained in details. For details, please refer to FastGpt Git.
1. Create Two Databases
Sealos provides a database tool that allows for visual deployment of databases.
1.1 Open the database tool
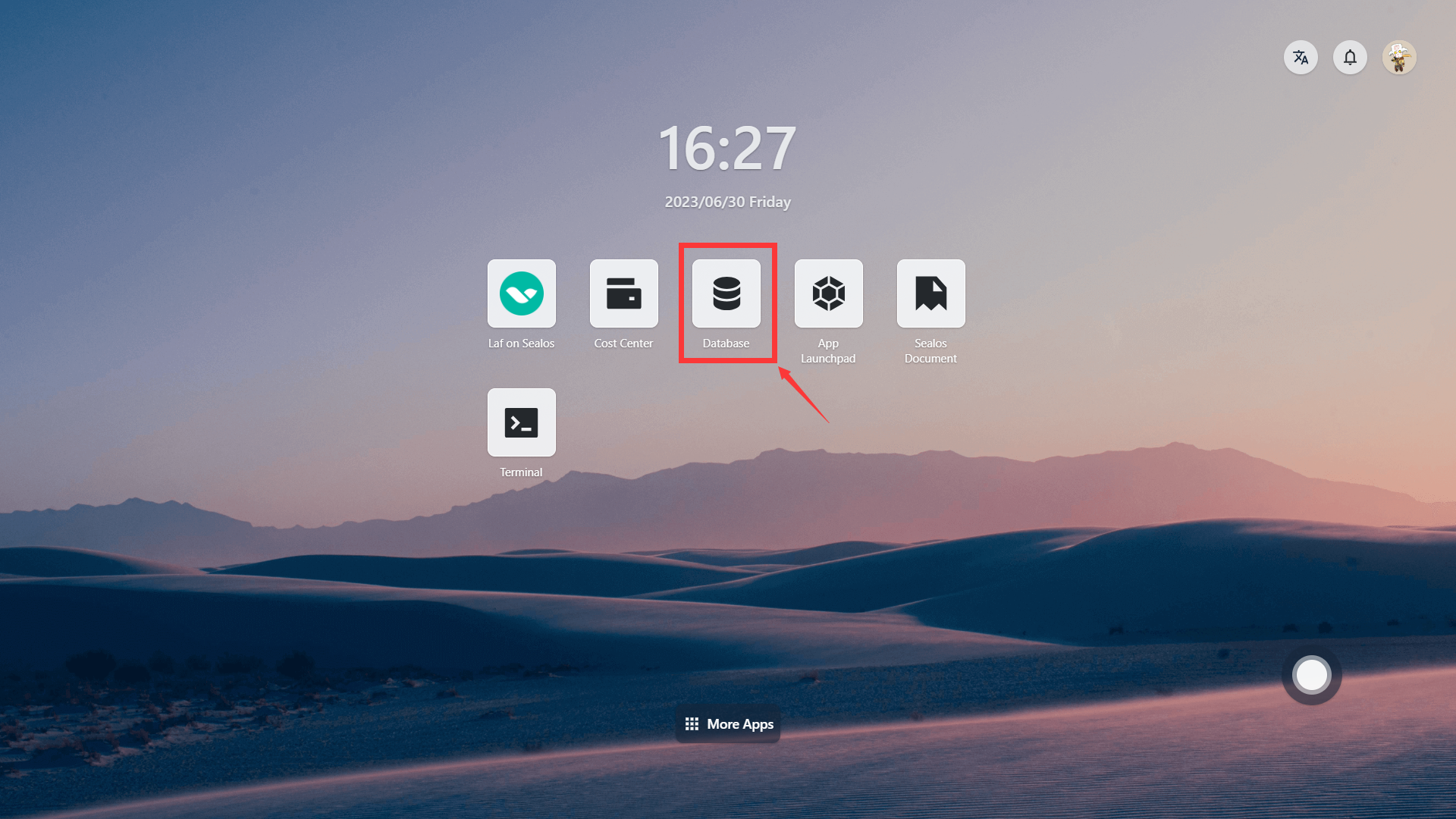
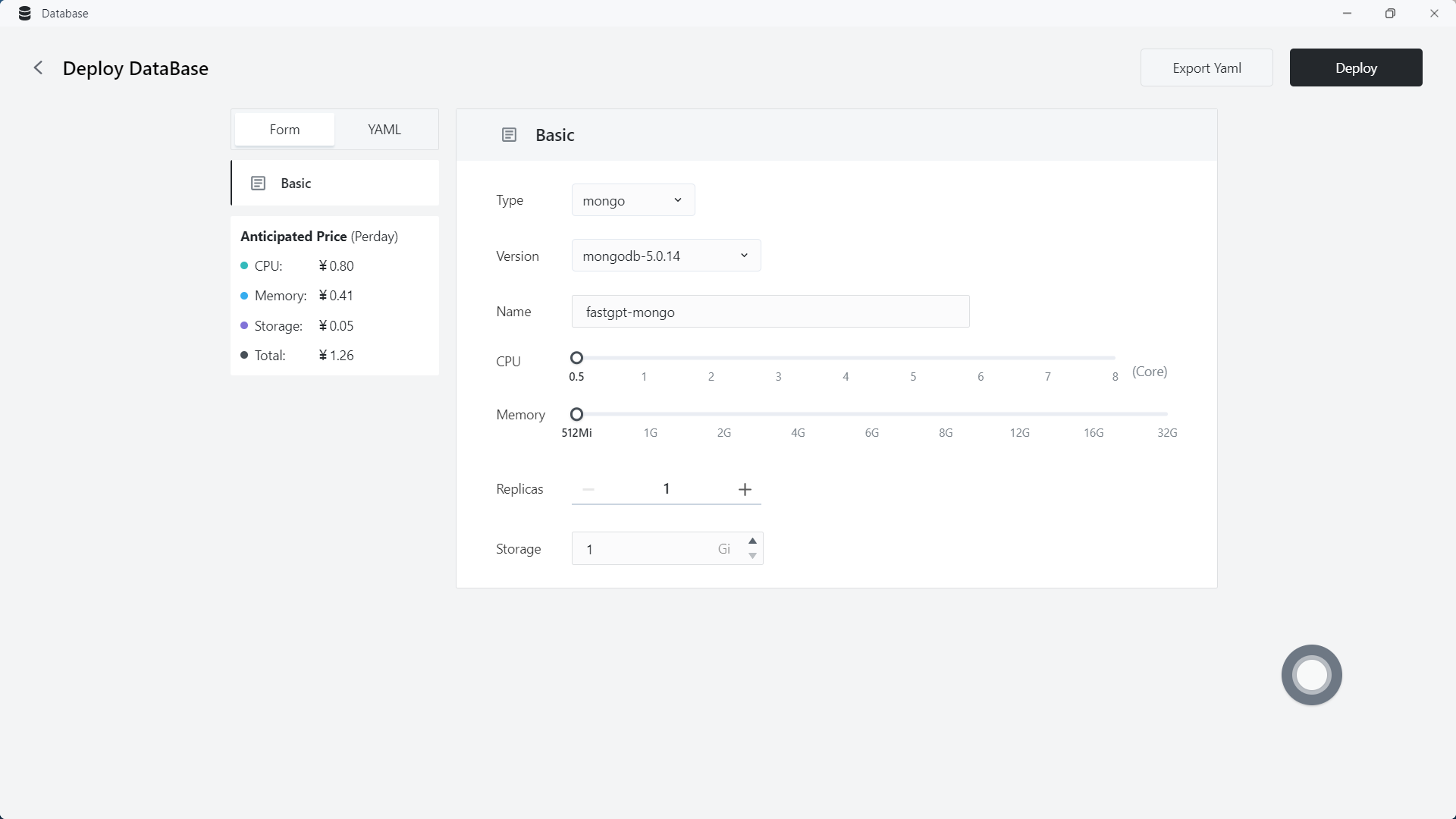
1.2 Create MongoDB database
Choose from three types of databases, and create a MongoDB first. It is recommended to choose a specification of 0.5C 512Mi or higher.
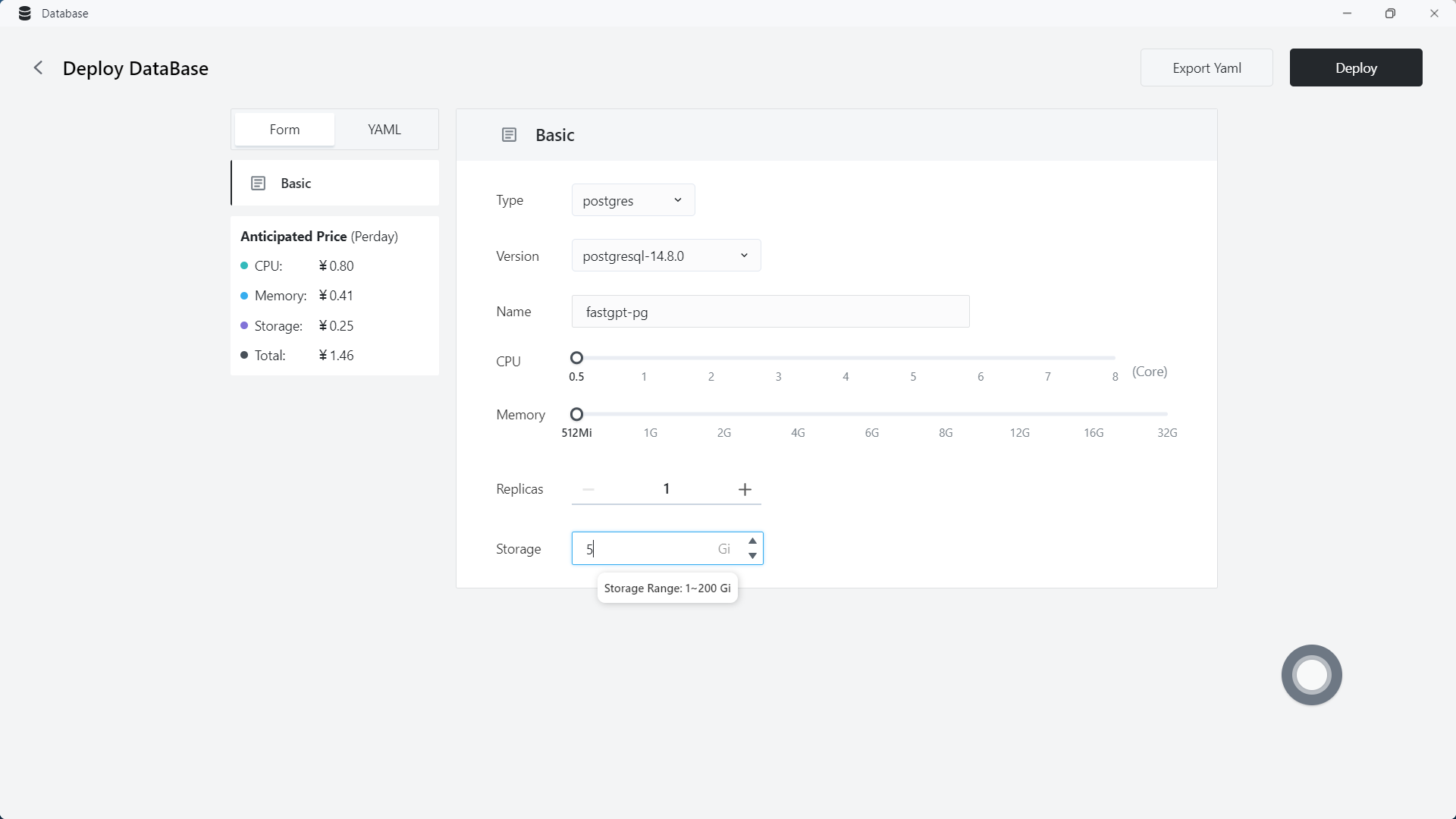
1.3 Create PostgreSQL database
Due to the need to store vector data in PostgreSQL, the required capacity is relatively large, and the initial capacity can be set to a larger size.
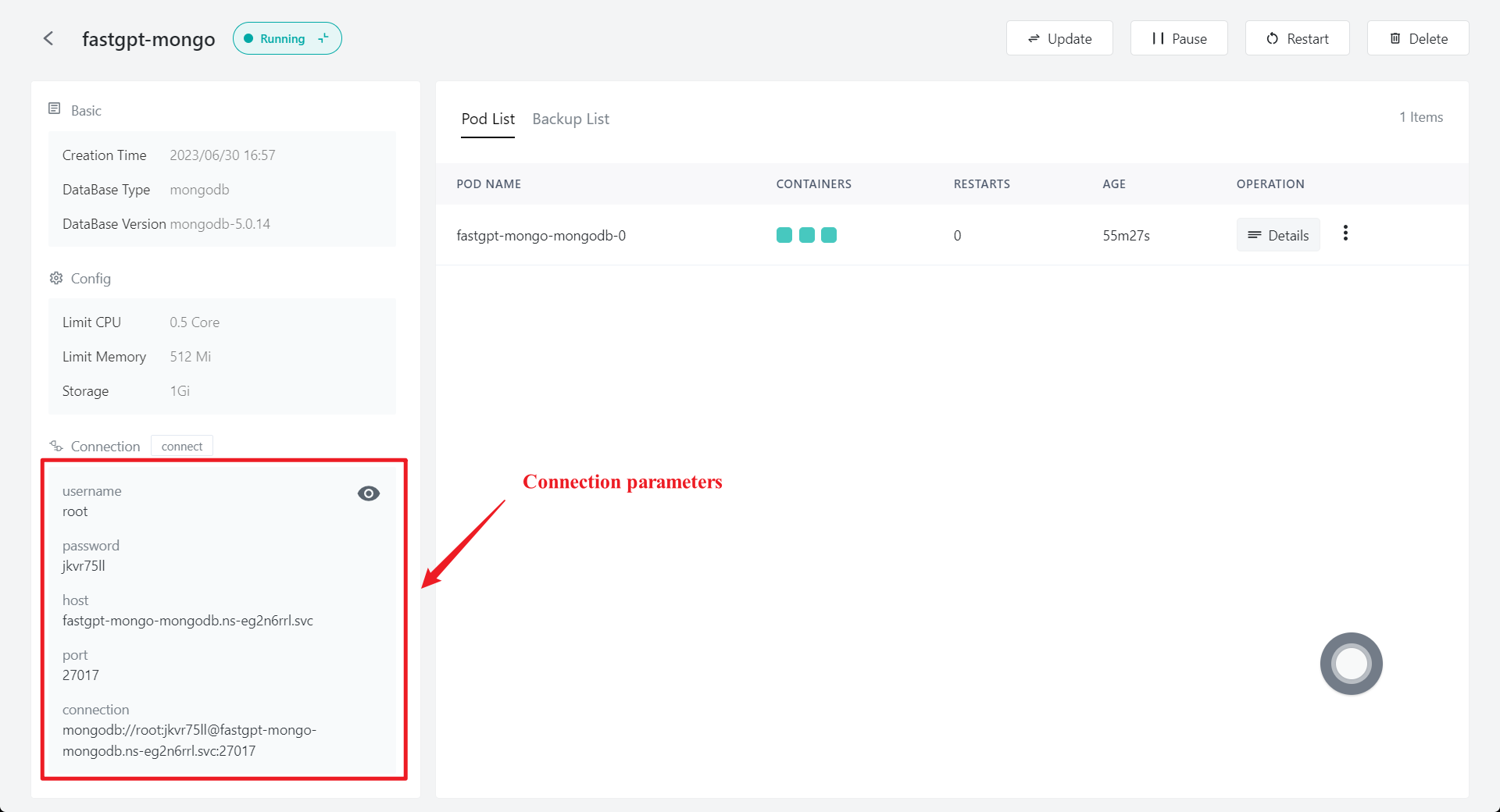
1.4 Check database connection parameters
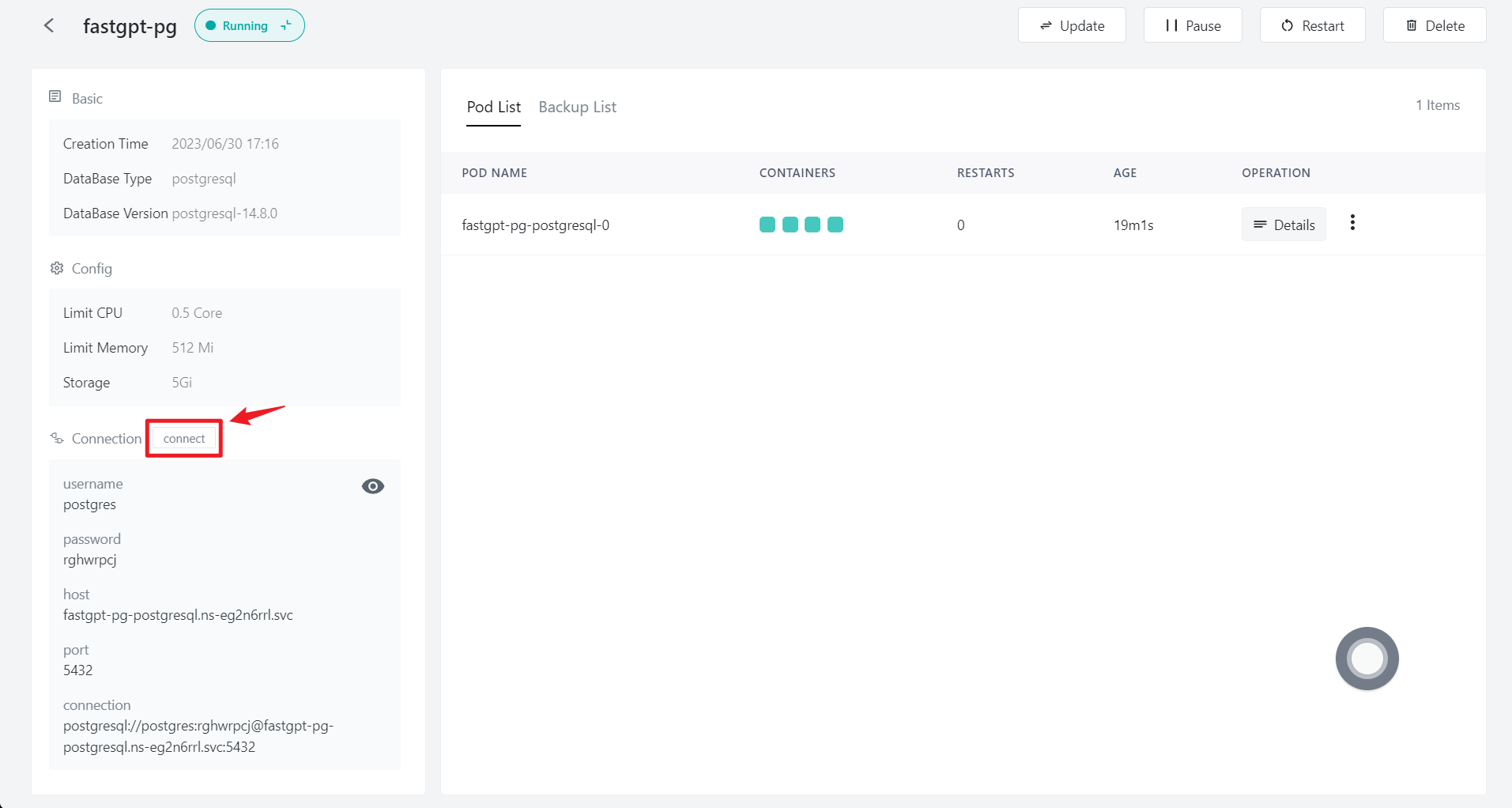
Click the database details and check the connection parameters of each database, including host, port, username, password and connectionUrl.
2. Initialize PostgreSQL Database
2.1 Connect to PostgreSQL database
Connect to the database with one click in the PostgreSQL database details.
2.2 Execute init.sql
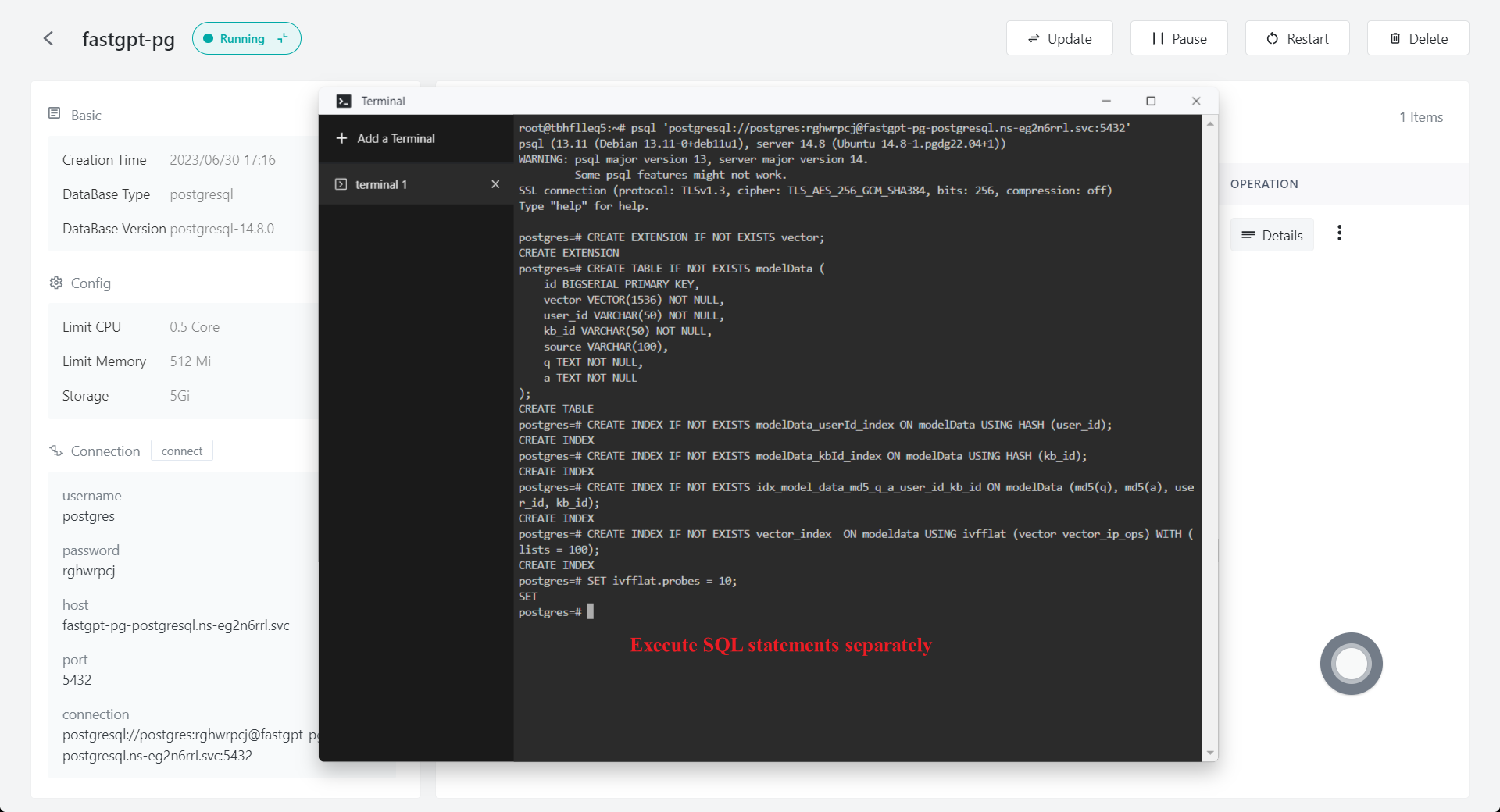
Copy and paste the following SQL into Terminal for execution. Paste using ctrl+shift+v. If there is an error with one-time paste, each SQL statement can be executed separately.
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS vector;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS modelData (
id BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
vector VECTOR(1536) NOT NULL,
user_id VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
kb_id VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
source VARCHAR(100),
q TEXT NOT NULL,
a TEXT NOT NULL
);
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS modelData_userId_index ON modelData USING HASH (user_id);
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS modelData_kbId_index ON modelData USING HASH (kb_id);
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS idx_model_data_md5_q_a_user_id_kb_id ON modelData (md5(q), md5(a), user_id, kb_id);
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS vector_index ON modeldata USING ivfflat (vector vector_ip_ops) WITH (lists = 100);
SET ivfflat.probes = 10;
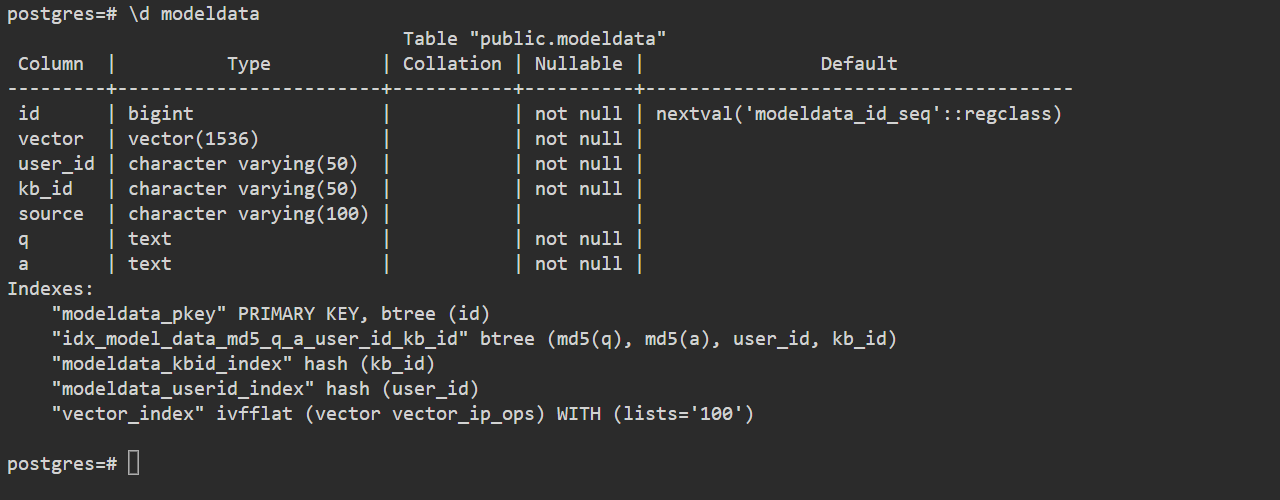
2.3 Verify initialization
Execute \d modeldata to check the details of the table to see if it is as expected.
3. Deploy FastGpt
Sealos provides App Launchpad that can quickly deploy single image services.
3.1 Open App Launchpad from Desktop
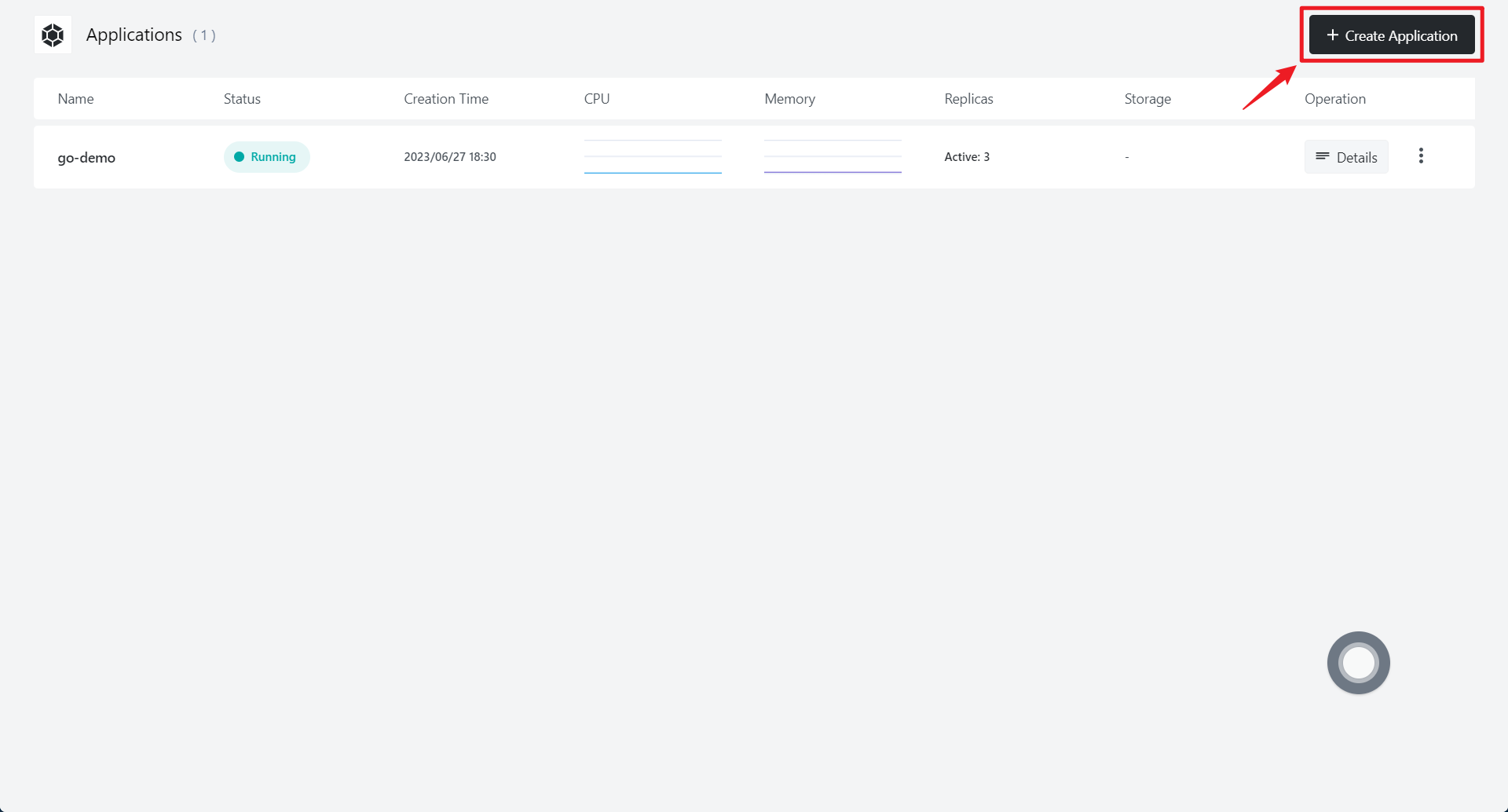
3.2 Click Create Application
3.3 Fill in the relevant parameters
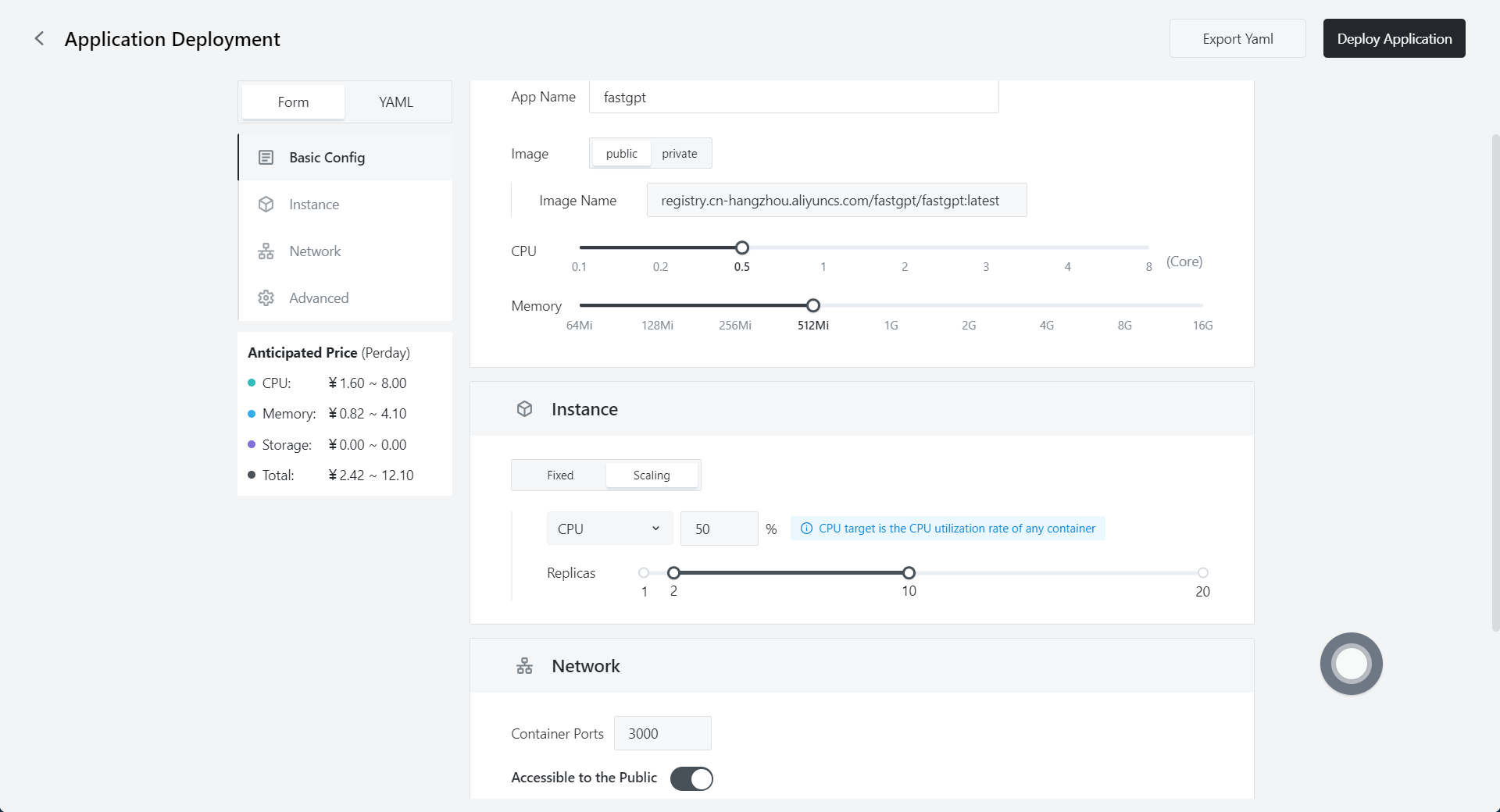
| variable names | description |
|---|---|
| Application Name | such as: fastgpt |
| Image Name | Official image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/fastgpt/fastgpt:latest |
| CPU and Memory | Depends on user's demand |
| container exposed port | 3000 |
| Accessible to the Public | Open「Accessible to the Public」and the domain name is automatically assigned and can be used directly or customized. |
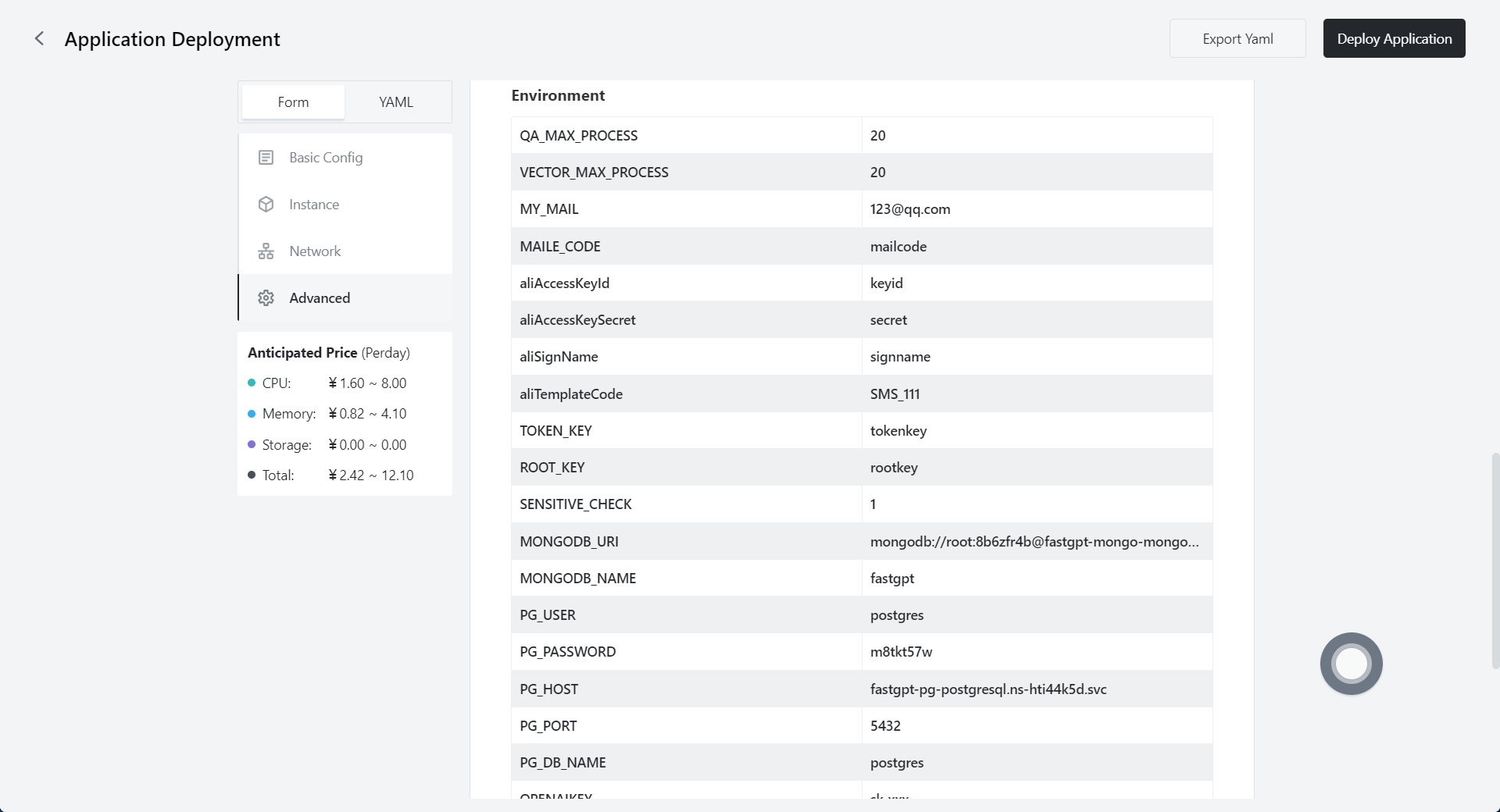
| Environment | Refer to FastGpt docker-compose.yaml For some variables in the database, directly copy the content in [1.4]. |
The following is an environment variable without annotations, which can be directly copied, modified, and used.
QA_MAX_PROCESS=20
VECTOR_MAX_PROCESS=20
MY_MAIL=123@qq.com
MAILE_CODE=mailcode
aliAccessKeyId=keyid
aliAccessKeySecret=secret
aliSignName=signname
aliTemplateCode=SMS_111
TOKEN_KEY=tokenkey
ROOT_KEY=rootkey
SENSITIVE_CHECK=1
MONGODB_URI=mongodb://root:8b6zfr4b@fastgpt-mongo-mongodb.ns-hti44k5d.svc:27017
MONGODB_NAME=fastgpt
PG_USER=postgres
PG_PASSWORD=m8tkt57w
PG_HOST=fastgpt-pg-postgresql.ns-hti44k5d.svc
PG_PORT=5432
PG_DB_NAME=postgres
OPENAIKEY=sk-xxx
OPENAI_TRAINING_KEY=sk-xxx
GPT4KEY=sk-xxx
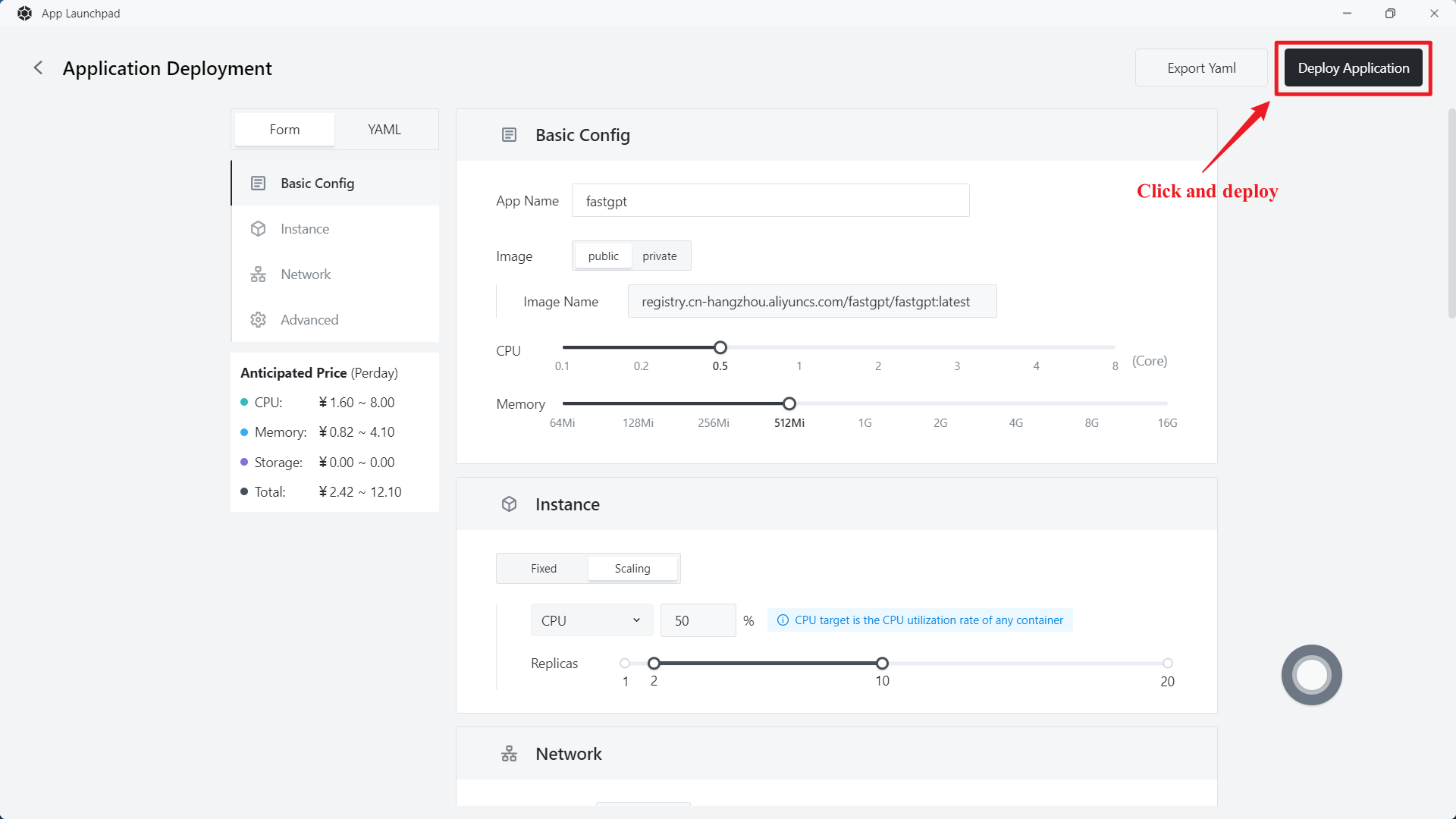
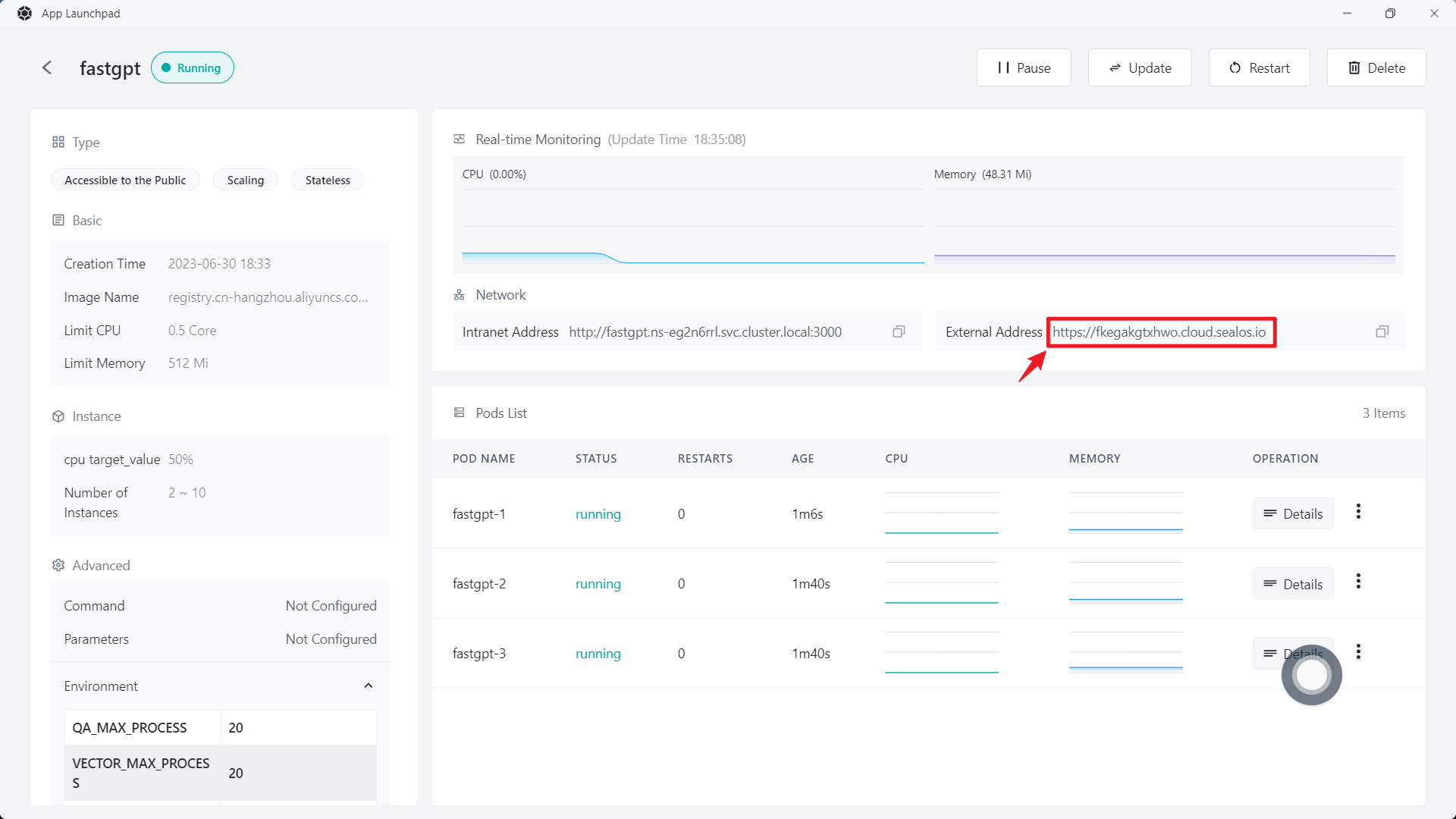
3.3 Access FastGpt
Access FastGpt through the external address or custom domain name provided by App Launchpad.